Russia Pushes Back on NATO Expansion
By Natylie Baldwin | Consortium News | July 9, 2016
Can Russian President Vladimir Putin turn the tables on NATO and the European Union in the Balkan states that are not yet members of the Atlanticist project? According to Filip Kovacevic, a political science professor who specializes in Russia and Eastern Europe, Putin has a plan. Some details were provided in an exclusive report in May on the nascent project by Russia to counter NATO expansion into the remaining Balkan countries that have not yet been swept into the Western alliance.
The plan has its origins in the grassroots movement that arose in the aftermath of the first Cold War, which called for non-alignment and cooperation with both East and West. Kovacevic describes the movement as follows:
Their members were generally young people who were enthusiastic, honest and genuinely committed to the public good, but were plagued by the lack of funding and faced with frequent media blackout and open discrimination. Nonetheless, their programs articulated the most promising and humane geopolitical vision for the Balkans. They conceptualized the Balkans as a territorial bridge between the West and the East rather than as the place of persistent confrontation, or the ‘line of fire’ as formulated by the U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry in 2015. They wanted the Balkans to become a force for peace and human dignity in the world. Their vision still remains the best option for the Balkans people.
This desire for non-alignment is understandable as a continuation of the policy of Tito’s Yugoslavia during the Cold War – the nation that several of the modern day Balkan states were a constituent part of. However, according to Kovacevic, these groups were easily overwhelmed, in terms of both financial and propaganda resources, in the 1990s by pro-NATO forces in the West.
In addition to providing resources to build up pro-NATO sentiment in the media and NGO sectors of these countries, financial resources and pressure was used to sway a large number of politicians to favor NATO membership, often in opposition to the general population’s views. Some of the unsavory forms of incentive or pressure include what amounts to blackmail and bribery, Kovacevic told me in an email interview:
This is a long-term process. In the U.S. intelligence community it is called ‘seeding.’ The intelligence scholar Roy Godson defines it as ‘identifying potential agents of influence’ at an early stage and then acting to advance their careers. This is typically done covertly, but there have been the historical examples of overt support. …
In the Balkans, the key role in the process of ‘seeding’ was accomplished by various institutes, conferences, retreats, grants, etc. For instance, I was told by a confidential source who participated in the same U.S.-NATO program, the long-time foreign minister and one-time prime minister of Montenegro, Igor Luksic, was a product of such a process. Luksic was chosen as a very young man to attend various conferences and retreats in Brussels and Washington and, after that, his political career really took off. All the while, he promoted the NATO agenda in Montenegro, even though this went against the will of the majority of the population.
Another example is Ranko Krivokapic who was the speaker of the Montenegrin Parliament for over a decade. He traveled on official business to the U.S. a few times every year and boasted to others that he had a lot of friends in the State Department and other institutions of the U.S. government. There are examples like these in Serbia, Macedonia, Croatia, etc. All over the Balkans.
There is also the fact the European Union has dovetailed its security arrangements to such an extent with NATO that new members are now virtually brought into the NATO structures by default. For example, Mahdi D. Nazemroaya, author of The Globalization of NATO, reports that the E.U.’s Security Strategy was absorbed into NATO during its annual summit in 2006. The emphasis of the summit was on securing energy resources with the goal of ‘co-managing the resources of the EU’s periphery from North Africa to the Caucuses.’ Also implied was the goal of redefining the E.U.’s security borders in synch with both Franco-German and Anglo-American economic and geopolitical interests.
Moreover, British Russia scholar Richard Sakwa, has pointed out that the security integration of the E.U. with NATO was further intensified with the ratification of the Treaty of Lisbon in 2007:
As for the comprehensive character, this is something that has been gaining in intensity in recent years as the foreign and security dimension of the E.U. has effectively merged with the Atlantic security community. The E.U.’s Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) since the Treaty of Lisbon (the “Reform Treaty”) of 13 December 2007, which came into effect in 2009, is now in substance part of an Atlantic system. Acceding countries are now required to align their defense and security policy with that of NATO, resulting in the effective ‘militarization’ of the E.U.
At this point, the forces seeking a non-aligned bridge role for the Balkan states are still very much around, but have suffered marginalization due to lack of resources to take on the powerful and now entrenched pro-NATO political forces. However, with increasing discontent with the weak economic prospects in certain Balkan states, combined with increasing instability in the E.U., it is believed that there is an opening for growth of the movement.
Economic Conditions in the Balkans
The Balkan states comprise Romania, Bulgaria, Albania, Macedonia, Serbia, Kosovo, Montenegro, Bosnia-Herzegovina and Greece.
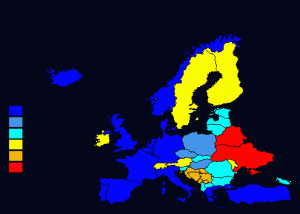
A map showing stages of NATO’s expansion. Dark blue showing original members; lighter blue the “round one” members; aqua the “round two” members; yellow represents neutral states; and brown and red otherwise aligned (including Ukraine, although that has changed since the 2014 U.S.-backed coup).
In 2007, Romania and Bulgaria became E.U. members (three years after joining NATO). Romania’s GDP has barely kept up with its 2008 rate and has a general unemployment rate of 6.4 percent, which sounds reasonable until you look at the youth unemployment rate of 21 percent, which doesn’t bode well.
Bulgaria, on the other hand, is not part of the Eurozone and has not adopted the euro as its currency. Its economic prospects since joining the E.U. have not been impressive either. In the midst of the financial crisis of 2009, its GDP contracted by 5.5 percent, with a current unemployment rate of 7 percent and youth unemployment at 17 percent. Bulgaria is also recognized as one of the union’s most corrupt countries.
Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Kosovo, Bosnia-Herzegovina and Albania are all in the process of E.U. integration, with a supposed approval rate of 80-90 percent among the respective populations of these countries (except for Serbia), despite the virtual rape of Greece and the lackluster performance of Romania and Bulgaria.
It should be noted that all three Balkan nations that are actual E.U. members have higher emigration than immigration rates, another indication that accession to the E.U. doesn’t necessarily translate into a prosperous future for the average person, particularly the young.
There is also the instability highlighted by the British people’s vote to leave the E.U., spurred by disgust with austerity measures imposed by unaccountable bureaucrats in Brussels along with an influx of immigrants – one-third from these poorer E.U. nations – which adversely affect lower-wage natives.
Even if the E.U. had a better track record of effectiveness in terms of improving economic conditions for the masses, it would have a very tall order with some of the prospective Balkan states. Macedonia, for example, has an unemployment rate between 24 and 25 percent as of January 2016, although it has improved from the 2005 high of 37 percent. Despite this improvement, Macedonia still has one of the lowest GDPs in Europe and 72 percent of its citizens claimed they manage their household income only with “difficulty” or “great difficulty” in 2012.
Bosnia-Herzegovina is still feeling the effects of the war of 1992 to 1995 that included major physical destruction of infrastructure and the bottoming out of its GDP. It currently suffers an unemployment rate of 42-43 percent.
Kosovo, a state that owes its existence to a NATO intervention, has 33 percent unemployment, a high crime rate and increasing political violence due to ethnic tensions and a growing ultra-nationalist movement. The Council of Europe compared the government of Kosovo to a mafia state in a 2010 report which revealed trafficking in human organs as well as drugs and weapons throughout Eastern Europe, even implicating the then-prime minister in the operation.
Russia’s Opening
Kovacevic states that the Atlanticist project of E.U. austerity economics and the enabling of Washington’s destabilizing wars via NATO is starting to chip away at its popularity among Balkan populations. He also says Putin is prepared to take advantage of this opening and, since the outbreak of the Ukraine crisis, has turned his attention “to the Balkans with political force and funding not seen since the days of tsar Nicholas II.”
This attention has manifested in the Lovcen Declaration, which was signed on May 6, by members of Russia’s largest political party, United Russia, and the opposition Democratic People’s Party in Montenegro in the village of Njegusi. Kovacevic explains:
One of the most powerful political figures in Montenegro, the metropolitan Amfilohije, the chief bishop of the Serbian Orthodox Church in Montenegro, was present at the signing and gave his blessing. Though in the past Amfilohije has been known to support the authoritarian and pro-NATO prime minister Milo Djukanovic around the election time, he has always publicly opposed NATO membership and has given fiery speeches on its ‘evil nature’ to the point of accusing NATO for continuing Hitler’s anti-Slavic project.
Even more importantly, Amfilohije’s involvement with the Lovcen Declaration reveals one of the fundamental components of Putin’s overall geopolitical plan – the nurturing and intensification of the religious Christian Orthodox connection between the Russians and the Orthodox peoples of the Balkans. This includes not [only] the Serbs, Montenegrins and Macedonians, but also the Greeks and Bulgarians whose states are in NATO and whose religious ‘awakening’ can easily subvert NATO from the inside.
Criticism and minimization of the project have set the tone in Western media, to the extent that it has been covered at all, particularly in relation to utilizing an opposition party for significant influence. But Kovacevic argues that such a dismissive attitude is disingenuous:
[T]he very same method has been used by the U.S. and NATO intelligence services to control the governments of East-Central European states since the collapse of communism. Countless small parties with just a handful of parliamentary deputies were formed with the money coming from the various ‘black budgets’ with the task of entering the governing coalition and then steering the entire government in the direction charted by their foreign founders and mentors.
These parties have had minimal public legitimacy, but have made a great political impact with their ‘blackmail’ potential. As they also don’t cost very much, the CIA, the MI6, and the BND regularly create them for every new election cycle.
Now the Russians (primarily, the SVR and the GRU) are using the same rulebook for their own geopolitical interests. In addition, however, Putin’s grand design for the Balkans embodied in the ANS is also likely to prove durable not only because it builds on the traditional cultural and religious ties linking Russia and the Balkans, but also because it rides on the wave of the enormous present popular dissatisfaction with the neoliberal Atlanticist political and economic status quo.
The fact that this declaration was signed in Montenegro is most relevant due to the fact that the country has been officially invited to join NATO, whose subsequent membership is treated in the West as a fait accompli. However, accession requires consensus approval by all current NATO members – one member could veto the move before completion of the process as happened with Macedonia when Greece vetoed their membership aspirations in 2008 when an invitation was to be offered at the Bucharest Summit – as well as approval by the population of Montenegro.
Joining any alliance treaty is arguably something that affects national sovereignty, which requires a referendum as Kovacevic, who is Montenegrin, explains:
The corrupt government of Milo Djukanovic is trying to avoid a national referendum because it knows that it does not have a majority support for NATO. If given a choice, the people of Montenegro would reject the protocol. The Constitution requires a referendum for all matters that affect national sovereignty, but Djukanovic is arguing falsely that NATO membership leaves Montenegrin sovereignty intact.
Kovacevic predicts that a show-down over NATO membership could create instability in the country: “[I]f he [Djukanovic] tries to push this decision through the Parliament (which he no doubt will), wide-scale strikes and demonstrations may take place all over the country. Whoever is pushing Montenegro in NATO is dangerously destabilizing the country in mid-to-long term.
If that happens, Washington may find for the first time in recent memory that forcing instability on a smaller country may ultimately accrue benefits to another great power, helping to facilitate a shift in geopolitics that it didn’t bargain on. As Nazemroaya comments in his book:
The [NATO] alliance is increasingly being viewed as a geopolitical extension of America, an arm of the Pentagon, and a synonym for an evolving American Empire. … Ultimately, NATO is slated to become an institutionalized military force. … Nevertheless, for every action there is a reaction and NATO’s actions have given rise to opposing trends. The Atlantic Alliance is increasingly coming into contact with the zone of Eurasia that is in the process of emerging with its own ideas and alliance. What this will lead to next is the question of the century.
Natylie Baldwin is co-author of Ukraine: Zbig’s Grand Chessboard & How the West Was Checkmated, available from Tayen Lane Publishing. In October of 2015, she traveled to 6 cities in the Russian Federation and has written several articles based on her conversations and interviews with a cross-section of Russians.


Good (long!) read; thank you. Given that Putin projects maturity, a non-chaotic foreign policy, and “belongs” in the neighborhood, he seems to be the chess master who has the best chance of moving toward “Checkmate!” But will the crazies’ follies lead to nuclear-war annihilation before the game is over?–at which point the game would be lost for everyone?
LikeLike